Quant Chalkboard: A New Way to Aggregate
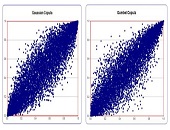
The Gumbel copula is the best way to aggregate losses in economic capital, says Yimin Yang, Director of Model Risk and Capital Management Practice at Protiviti, a global consulting firm. “This copula has asymmetrical behaviour and can model fat tails the best” of the numerous copulas he has tried recently. He was speaking at a GARP webinar on August 20, 2013. Yang began by explaining that a copula was a broad class of mathematical function that could be used to describe the joint distribution function between two or more other functions. Such a joint cumulative distribution function (CDF) must determine […]
Risk Models: From Governance to Validation: Part 3. Examples
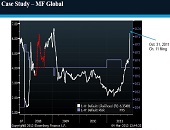
“The calculation of the spread on the tranches is quite involved but essentially boils down to dependencies between names,” said Frederic Siboulet, Principal at iEpsilon and the third of three speakers at a GARP webinar on risk models held June 11, 2013. The tranches in structured credit products he referred to were apparently diversified, but in reality not so. Siboulet chose to illustrate the subtle and embedded risk of models with actual structured product examples. In particular, he said that “We must not overlook the importance of the parameters and their interpretation.” The first example involved stressed correlation within a […]
Risk Models From Governance to Validation: Part 2. A Model of Model Management
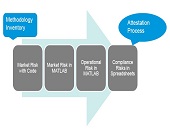
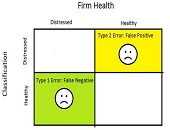
No longer should a firm just use financial models; it should have a “model of model management,” said Donna Howe, Chief Risk Officer at Sovereign Bank. She was the second of three speakers at a June 11, 2013 webinar on risk models organized by the Global Association of Risk Professionals (GARP). Such a “meta-model” would help a firm sort and track models. Howe said that risk models must be understood within the wider frame of compliance and other non-prudential risk. Model parsimony, or Occam’s razor, that was recommended by the first speaker, is good but in the real world “cannot […]
Risk Models From Governance to Validation: Part 1. Don’t Forget the Story
The best practices of risk models–and model building–boil down to one thing: “we can’t forget the story behind it,” said Peter Went, VP, Banking Risk Management Programs at GARP. He was the first of three speakers at a GARP webinar on risk models held June 11, 2013. “There must always be a qualitative story expressible in quantitative terms.” And, vice versa, since any model reduces the complexities of the real world into snippets of mathematical relationships, the opposite must hold true. Went, a trained econometrist, described three main types of models. Fundamental models are based on rules relating basic variables […]
Managing Model Risk: Part 3. Collective Hubris
There are more things in heaven and earth, Horatio, Than are dreamt of in your philosophy. – Wm. Shakespeare, Hamlet, Act 1, Scene 5. “We are building the language in which to discuss model risk,” said Boris Deychman, Director of Model, Market and Operational Risk Management at RBS Citizens Financial Group. He drew an analogy with the world of wine experts, who have developed specific vocabulary to talk about aroma and taste. “They don’t say just: this tastes like wine.” Deychman was the third and final speaker of a panel invited by the Global Association of Risk Professionals to discuss […]
Managing Model Risk: Part 2. The Impact of Basel III
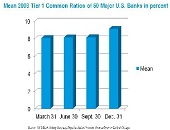
“More consideration must be made for regulatory capital changes that focus on small but potentially devastating risks or risk factors,” said Peter Went, VP, Banking Risk Management Programs at GARP. He was speaking about Basel III and its impact on modelling regulatory capital at a webinar on January 29, 2013, organized by the Global Association of Risk Professionals to discuss model risk management. Went mentioned three developments in the Basel III that directly impact capital models and model risk in regulatory capital determination. First, Basel III introduces a risk-invariant leverage ratio of 3 percent in recognition that models may be […]
Managing Model Risk: Part 1. “Models are Always Wrong”
“Models are always wrong,” said Joe Pimbley, Principal at Maxwell Consulting, via webinar on January 29, 2013. He was the first of a panel of three speakers invited by the Global Association of Risk Professionals to discuss model risk, what it is, and how to assess and validate it after the financial crisis. Models are always wrong, Pimbley clarified, because they are only simplifications. “Wrongness” he defined as some type of error or omission that materially impacts the results as understood by the user. A model can be wrong because the meaning of the result differs from that understood by […]
Contingent Capital: The Case for COERCs. Part 1
Contingent convertible bonds, or “cocobonds,” are bonds that convert into equity when the market value of capital falls below a trigger level. A major problem with cocobonds is that “the conversion trigger is based on the capital ratio, which is known to be a poor indicator of financial distress,” said Theo Vermaelen, Professor of Finance at INSEAD. He was the first speaker at the November 29, 2012 webinar held by the Global Association of Risk Professionals (GARP) on the subject of Call Option Enhanced Reverse Convertible (COERC) bonds. Vermaelen referred to a case in point: a Credit Suisse cocobond issued […]